AC test transformer principles form the foundation for understanding how these specialized transformers operate in high-voltage testing environments. These transformers are designed to generate alternating current (AC) voltages at specific magnitudes and frequencies to test the insulation and performance of electrical equipment. Grasping the fundamental working principles allows engineers to ensure safety, accuracy, and reliability during electrical tests.
Fundamental Operating Mechanism
At the heart of the AC test transformer principles lies electromagnetic induction. The primary coil receives a low voltage AC input, inducing a magnetic flux within the transformer core. This magnetic flux then induces a higher voltage in the secondary coil, thus stepping up the voltage. The basic principle is similar to general transformers but tailored for controlled, high-voltage output essential for testing purposes.
Voltage Transformation and Regulation
AC test transformers are designed with precise voltage transformation ratios derived from AC test transformer principles. These ratios ensure that the output voltage is accurately stepped up or stepped down as required. The transformer incorporates tap changers and voltage regulators to fine-tune the output, maintaining consistent voltage levels critical for reliable electrical testing.
Frequency Considerations in AC Testing
Frequency plays a vital role in AC test transformer principles. Most AC test transformers operate at standard mains frequency (50 or 60 Hz), but some specialized applications require varying frequencies. Understanding how frequency affects impedance, losses, and heating in the transformer is crucial for applying the correct test conditions during diagnostic procedures.
Core Construction and Magnetic Properties
The core material and design significantly impact the operational efficiency governed by AC test transformer principles. Typically constructed using high-grade silicon steel laminations, the core minimizes hysteresis and eddy current losses. Proper core design ensures the magnetic flux remains confined within the core, optimizing voltage output and reducing undesirable heat generation during prolonged testing.
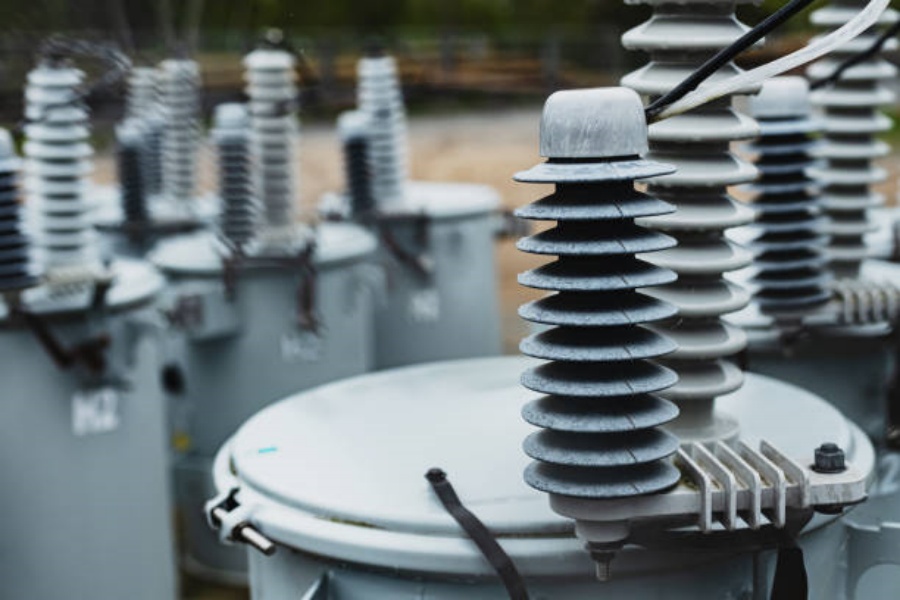
Insulation System and Safety Mechanisms
Since AC test transformers deal with high voltages, robust insulation is imperative. AC test transformer principles emphasize using insulation materials that withstand electrical stress, thermal changes, and mechanical wear. Safety features such as protective relays, current limiting resistors, and discharge devices ensure secure operation and prevent damage to the transformer or the equipment under test.
Load Characteristics and Impact on Performance
The load connected during testing influences the transformer's behavior following AC test transformer principles. Resistive, inductive, or capacitive loads affect voltage regulation and current flow, potentially causing voltage drops or distortions. Engineers must understand load implications to accurately interpret test results and avoid overloading the transformer.
Thermal Management in AC Test Transformers
Heat generation is an unavoidable byproduct during transformer operation. AC test transformer principles include thermal management strategies like oil-immersion cooling or forced air cooling to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Effective thermal dissipation enhances longevity while maintaining consistent output during continuous testing cycles.
Applications Derived from AC Test Transformer Principles
These transformers find extensive use in electrical power systems for testing insulation strength, circuit breakers, cables, and apparatus. The principles underpin standard testing procedures such as hipot testing, dielectric tests, and withstand voltage tests, ensuring equipment reliability and compliance with international standards.
Future Trends and Innovations in AC Test Transformers
Advancements based on AC test transformer principles focus on improved efficiency, compact design, and digital integration. Innovations include solid-state control for voltage regulation, enhanced insulation materials, and smart monitoring systems. These developments aim to simplify testing protocols and increase the precision and safety of electrical equipment testing.
Quote Inquiry
contact us